Physics 5 



A Complex Class and the Mandelbrot Set
During lecture we delved further into abstract data types (ADTs) and built one called Complex for dealing with complex numbers. Building and testing the class was accomplished by organizing functions in three files: one for the class prototypes, another for the class definitions and a third for the main() function, or, in the Dark GDK environment, the DarkGDK() function where we could test the Class.
Below is the complex.h
file with the Complex class creation with the public and private
sections. It’s not necessary to have
private parts, but it’s considered good practice. It’s called data hiding and the idea is that
a programmer using a class needs to have no knowledge of how that class is
actually implemented, or of how the private attributes are actually stored. In
C++ terms this means that a programmer needs only know the public interface to
the class and has no need to know anything at all about how the private parts
are put together.
The programmer developing a class specifies exactly how that class can be used.
The goal is to make it impossible to use it in a way that would produce
incorrect results. Testing is made easier because the interface is often quite
small it is much easier to thoroughly test a small
well-defined interface than it is to test a large unstructured program.
The header file typically just contains prototypes, as shown here:
|
// Complex.h
class Complex { public: Complex(float=1, float=0); Complex operator+(Complex &rhp); Complex operator-(Complex &rhp); Complex operator*(Complex &rhp); Complex operator/(Complex &rhp); float sqrModulus(); Complex squareRoot(); void print(int, int); private: float _real; float _imag; float _modulus; float _argument; float _mod(); float _arg(); }; |
The constructor has the same name as the class, has no return value and is
given here the default initialization values (float=1, float=0)
so that, if a Complex is created
without values, the default Complex
is 1+0i.
The overloaded binary operators +, ,*
and / are set up here as member functions with the left-hand operand as the one
that “owns the cal”
that is, the left hand operand invokes the
member function +,
,
* or / while the right hand operand is the input to the function, and the
return value is a the sum or difference of the left and right operands, also a Complex.
Prototypes for member functions sqrModulus() and squreRoot() and print() are also provided. For clarity, the definitions of these functions are provided in a separate file, shown below:
|
// ComplexMethods.cpp
#include "Complex.h" #include "DarkGDK.h"
Complex::Complex(float real, float imag) : _real(real), _imag(imag) {}
Complex Complex::operator+(Complex &rhp) { Complex temp(_real + rhp._real,_imag + rhp._imag); return temp; }
Complex Complex::operator-(Complex &rhp) { Complex temp(_real - rhp._real,_imag - rhp._imag); return temp; }
Complex Complex::operator*(Complex &rhp) { Complex temp(_real*rhp._real - _imag*rhp._imag, _real*rhp._imag + _imag*rhp._real); return temp; }
Complex Complex::operator/(Complex &rhp) { // dividing by a complex involves multiplying by the conjugate of divisor float sqrMod = rhp._real*rhp._real + rhp._imag*rhp._imag; Complex temp((_real*rhp._real + _imag*rhp._imag)/sqrMod, (_imag*rhp._real - _real*rhp._imag)/sqrMod); return temp; }
float Complex::sqrModulus() { return _real*_real + _imag*_imag; }
Complex Complex::squareRoot() { float tol = 1.e-10; Complex z(_real,_imag); Complex sqrt = z; Complex Two(2.,0.1); Complex temp = z/Two; while((sqrt - temp).sqrModulus() > tol) { sqrt = temp; temp = (sqrt + z/sqrt)/Two; } return sqrt; }
float Complex::_mod() { // uses the sqrt() function in DarkGDK.h return sqrt(_real*_real + _imag*_imag); }
void Complex::print(int h, int v) { dbText(h, v, dbStr(_real)); dbText(h + 8*14, v, " + "); dbText(h + 8*14 + 8*3, v, dbStr(_imag)); dbText(h + 8*28 + 8*3, v, " i"); } |
And finally, the code to test the Complex class. Try experimenting with different values of the parameters defining width, height, the initial values of ULx, ULy, LRx, LRy
|
// Hagopian's complexMain.cpp
#include "Complex.h" #include "DarkGDK.h"
int mandelbrot(Complex); void drawScreen(float, float, float, float, int, int);
DWORD red = dbRGB(255,0,0); //global scope DWORD blue = dbRGB(0,0,255); DWORD black = dbRGB(0,0,0); DWORD white = dbRGB(255,255,255);
void DarkGDK() { dbSyncOn(); dbSyncRate(1); // 1 per sec is pretty slow // variables for the window's width, height and color depth int width = 640, height = 480, colorDepth = dbScreenDepth(); // Set the womdpw size and color depth dbSetDisplayMode(width, height, colorDepth); //dbText(10,10,"Enter the coords of upper left corner of window: "); float mouseULx = 0, ULx = -1.; //these are hardwired here, but may float mouseULy = 0, ULy = 1.; //also be user supplied //dbText(10,20,"Enter the coords of lower right corner of window: "); float mouseLRx = width, LRx = 0.; //atoi(dbInput()); float mouseLRy = height, LRy = 0.; //atoi(dbInput()); float tempULx, tempULy, tempLRx, tempLRy; // drawScreen draws the mandelbrot fractal set drawScreen(ULx, ULy, LRx, LRy, width, height); /*dbInk(black,red); // testing functions Complex a; Complex b(0); Complex c(1); Complex d(2,2); Complex e(-2,2); Complex f(-2,-2); Complex g(-2,2); a.squareRoot().print(10,10); b.squareRoot().print(10,22); c.squareRoot().print(10,34); d.squareRoot().print(10,46); e.squareRoot().print(10,58); f.squareRoot().print(10,70); g.squareRoot().print(10,82); */ //dbWaitKey(); bool dragging = false; // The game loop while ( LoopGDK() ) { // won't happen 1st time thru the loop after mouse clicked // since dragging is false if(dbMouseClick() == 1 && dragging) { mouseLRx = dbMouseX(); // 2nd click for lower right corner mouseLRy = dbMouseY(); // we have both corners and we can tempULx = mouseULx*(LRx - ULx)/width; // compute dimensions tempLRx = mouseLRx*(LRx - ULx)/width; // of complex plane tempULy = mouseULy*(LRy - ULy)/height; // window on the tempLRy = mouseLRy*(LRy - ULy)/height; // Mandelbrot set ULx = tempULx; ULy = tempULy; LRx = tempLRx; LRy = tempLRy; // draw the mandelbrot set
drawScreen(ULx, ULy, LRx, LRy, width, height); } else if(dbMouseClick() == 1) { // first click while not dragging tempULx = dbMouseX(); // get upper left corner tempULy = dbMouseY(); // user must know to do this? dragging = true; // We are now dragging } else dragging = false; // Print data to screen for debugging dbInk(white,white); dbBox(0,0,240,90); dbInk(black,white); dbText(10,10,"mouseULx = "); dbText (130, 10, dbStr(mouseULx)); dbText(10,20,"mouseULy = "); dbText (130, 20, dbStr(mouseULy)); dbText(10,30,"mouseLRx = "); dbText (130, 30, dbStr(mouseLRx)); dbText(10,40,"mouseLRy = "); dbText (130, 40, dbStr(mouseLRy)); dbText(10,50,"ULx = "); dbText (97, 50, dbStr(ULx)); dbText(10,60,"ULy = "); dbText (97, 60, dbStr(ULy)); dbText(10,70,"LRx = "); dbText (97, 70, dbStr(LRx)); dbText(10,80,"LRy = "); dbText (97, 80, dbStr(LRy)); dbSync(); } // end while } // end DarkGDK()
// The iterative scheme will either diverge to infinity // or converge to a point interior to the Mandelbrot set, // or wander chaotically around the perimeter of the set // Input is complex number in complex plane // Output is the number of iterations of mandelbrot int mandelbrot(Complex c) { bool diverge; Complex z; z = c; if (z.sqrModulus() > 5.1) return 0; // not in Mandelbrot set int count = 0; do { z = z*z + c; // Mandelbrot iteration ++count; // higher counts affect colors plotted } while(z.sqrModulus() < 5.1 && count < 400); if (count > 10) return count; // return 0; //interior }
void drawScreen(float ULx, float ULy, float
LRx, float LRy, // Walk through the default window by steps of 1 pixel float real, imag; int color; for(int i = 0; i < width; i += 1) { for(int j = 0; j < height; j += 1) { real = ULx + (float)i*(LRx - ULx)/width; imag = ULy + (float)j*(LRy - ULy)/height; Complex c(real,imag); // Complex for initial point color = mandelbrot(c); // mandelbrot returns color if(color == 0) { dbInk(white,white); dbDot(i,j); } else { dbInk(dbRGB(255 - 5*color,20*color,5*color),white); dbDot(i,j); } /* // This is the code we developed in class if(mandelbrot(c)) { dbInk(dbRGB(red,black); dbDot(i,j); } else { dbInk(blue,black); dbDot(i,j); }*/ } // end for } // end for } |
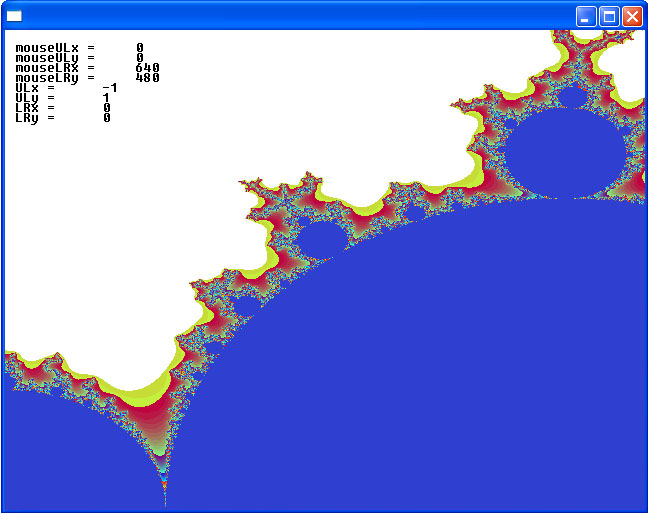
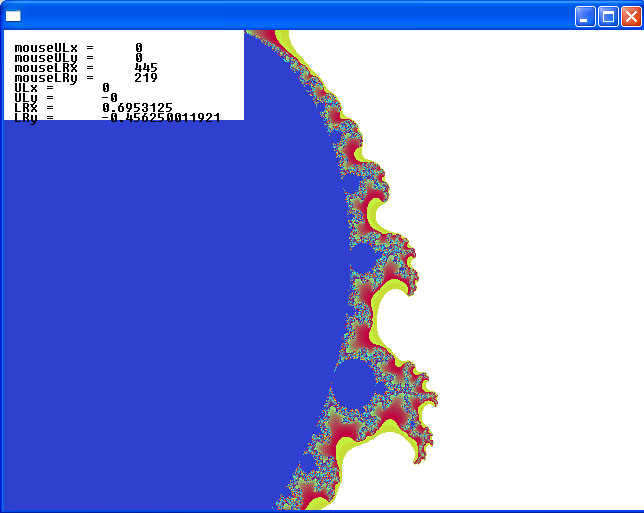
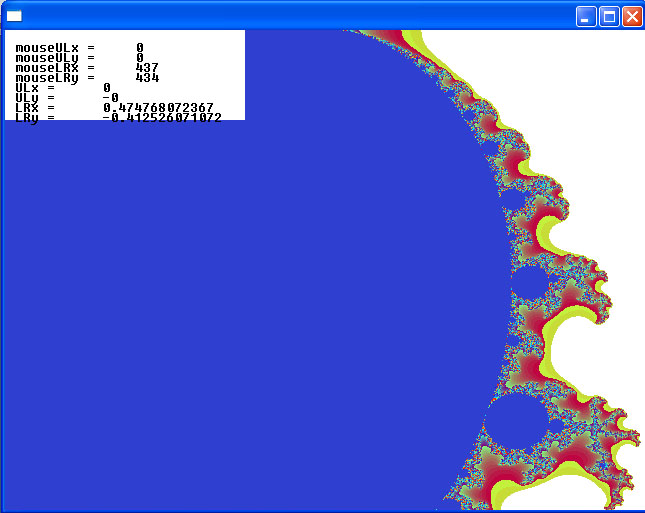
The idea is to use the mouse to click and drag out a rectangle to zoom in on. There seem to be some bugs…can you fix them?
Here are some pictures showing one run of the program. As you can see the program uses the upper left corner of the screen to display some of the values obtained by mouse clicks and computations on the mouse clicks. Why does LRy come out negative? Plus why do we not get what we seem to choose? As you can see, it’s a work in progress.
|
|
|
|
|
|