Math 5 Trigonometry
Final Exam Problems
Fall ’07
|
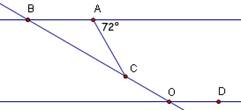
1.
In the diagram at right, assume that a.
What is the degree measure of b.
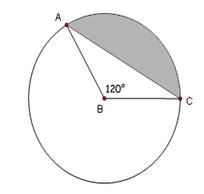
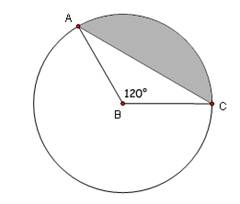
If 2.
Central angle a. If B is at the origin and C is at (1,0) in a rectangular coordinate system, what could the coordinates of A be? b. What is the length of AC? c. What is the area of the shaded region? |
|
|
3.
Given a. Find a formula for the inverse function. b.
Graph |
|
|
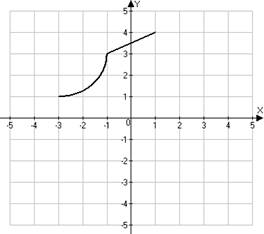
4.
Given the graph of a.
b.
c.
d.
|
|
5.
If and the terminal point determined by t is in the 2nd quadrant,
find each of these:
a.
.
b.
.
c.
d.
6.
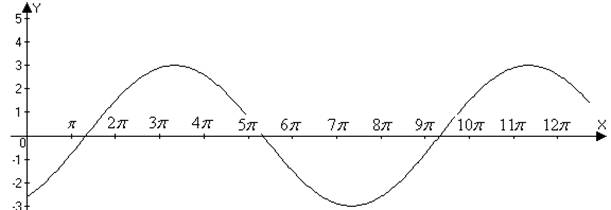
Sketch a graph for the sinusoidal function .
Also, state the period, amplitude and phase angle.
7. Find the side labeled x:
a.
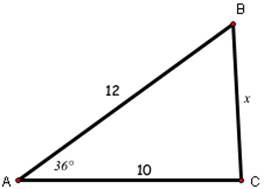 b.
b.
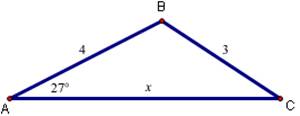
8.
Consider the vectors and
a. Draw the vectors together in the coordinate plane (take the origin as the original point for each).
b.
Use the formula to approximate (four digits) the radian
measure of the angle
between these vectors.
c.
Find the length of
9.
Consider
a. Find the domain of the function.
b. Find the range of the function.
c.
Sketch a graph of the function showing two periods.
10. A
potter’s wheel with radius 6 inches spins at 180 rpm. Find the angular and linear speeds of a point
on the rim of the wheel in feet per
second.
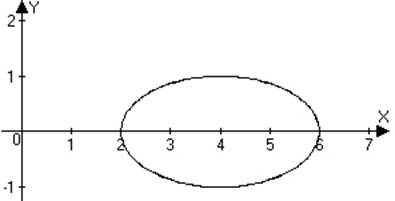
11. Write the conic in standard form and sketch a graph indicating key features:
a.
b.
Math 5 Trigonometry
Final Exam Solutions
Fall ’07
|
12. In
the diagram at right, assume that a.
What is the degree measure of b.
If 13. Central
angle a.
If B is at
the origin and C is at (1,0) in a
rectangular coordinate system, what could the coordinates of A be? |
|
b.
What is the length of AC? SOLN:
c.
What is the area of the shaded region? SOLN:
Area of sector area of triangle =
|
14. Given
a.
Find a formula for the inverse function. b.
Graph |
|
|
15. Given
the graph of a.
b.
c.
d.
|
|
16. If
and the terminal point determined by t is in the 2nd quadrant,
find each of these:
a.
. SOLN:
b.
. SOLN:
c.
SOLN:
d.
SOLN:
17. Sketch
a graph for the sinusoidal function . Also, state the period, amplitude
and phase angle. SOLN: Period = 8π, amplitude = 3 and phase angle =
4π/3.
18. Find the side labeled x:
a.
 b.
b. 
(a)
(b)
19. Consider
the vectors and
a.
Draw the vectors together in the coordinate plane (take
the origin as the original point for each).
SOLN: 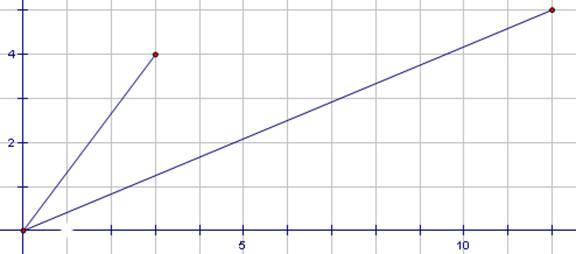
b.
Use the formula to approximate (four digits) the radian
measure of the angle
between these vectors.
SOLN:
c.
Find the length of
SOLN:
20. Consider
a.
Find the domain of the function. Coup de tat
SOLN: The domain of the function is where
b.
Find the range of the function.
The range is all reals,
c.
Sketch a graph of the function showing two periods.
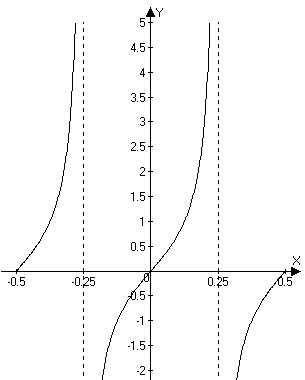
21. A
potter’s wheel with radius 6 inches spins at 180 rpm. Find the angular and linear speeds of a point
on the rim of the wheel in feet per second.
SOLN:
22. Write the conic in standard form and sketch a graph indicating key features:
a.
SOLN:
whence the center is ,
,
,
,
vertices are at
and the asymptotes are along
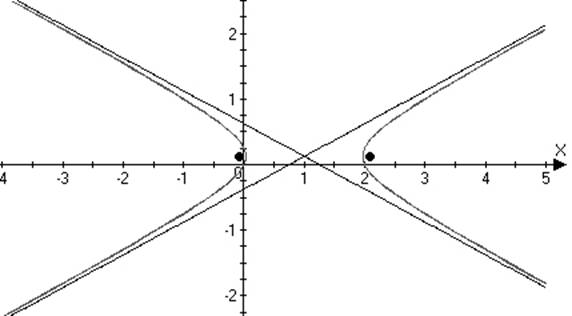
b.
SOLN: This is equivalent to ,
which means that a = 2, b = 1 and so
.
Major axis vertices are at (0,2) and (0,6) while minor axis vertices are at
(4,1) and (4, 1).