|
Math 5  Trigonometry Trigonometry  Chapter 1 Test Chapter 1 Test  Fall ’08 Name__________________________ Fall ’08 Name__________________________
Show all work for credit.
Explain your answers in detail. Write all responses on separate paper.
|
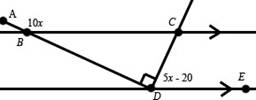
1. What
is the degree measure of angle x
in the figure at right? Explain how
you know.
|

|
|
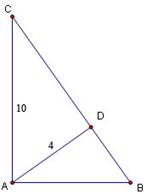
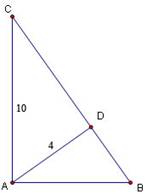
2. Consider
the diagram at right and assume that   and that and that   . .
a. Prove
that  
b. If
AC = 10 and AD = 4, find the perimeter of   . Hint: If you find CD then you’ll have the ratios . Hint: If you find CD then you’ll have the ratios   for all three triangles. for all three triangles.
|
|
|
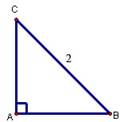
3. Draw
an isosceles right triangle whose hypotenuse has length 2 and label the
vertices A, B, and C. Find the perimeter and area of the
triangle and simplify these.
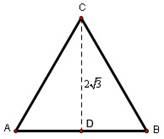
4. Draw
an equilateral triangle with height =   and label the vertices A, B, and C. Find the perimeter and area of the
triangle. and label the vertices A, B, and C. Find the perimeter and area of the
triangle.
|
|
5. Given
the triangle shown at right, with AC
= AB and   ,
show that ,
show that  
|

|
|
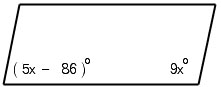
6. The
figure at right is a parallelogram.
Find x.
|
|
|
7. Find
the arc length that subtends a central angle of 60° in a circle of radius
12 cm.
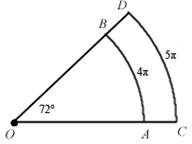
8. Find
the area of region ACDB bounded
by concentric arcs
  = 4π cm and CD = 5π cm as shown at right. = 4π cm and CD = 5π cm as shown at right.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Math 5  Fall ’08 Fall ’08  Chapter 1 Test Solutions Chapter 1 Test Solutions
|
1. What
is the degree measure of angle x
in the figure at right? Explain how
you know.
ANS: When the transversal   crosses the parallels it creates equal
corresponding angles, so crosses the parallels it creates equal
corresponding angles, so    
|
|
|
2. Consider
the diagram at right and assume that   and that and that   . .
a. Prove
that  
ANS: Since   , ,
  . .
Also, the two acute angles of a right triangle are complementary, so     and thus and thus   . Two congruent angles are enough to
conclude that the triangles are similar. . Two congruent angles are enough to
conclude that the triangles are similar.
|
|
|
b. If AC
= 10 and AD = 4, find the
perimeter of   . .
ANS: CD =   .
Clearly all three triangles shown are similar. Thus .
Clearly all three triangles shown are similar. Thus   . Also . Also   and the perimeter of and the perimeter of   is 4+ is 4+  
|
|
3. Draw
an isosceles right triangle whose hypotenuse has length 2 and label the
vertices A, B, and C. Find the perimeter and area of the
triangle and simplify these.
ANS: Since AB = AC are the legs of a right triangle
with hypotenuse of length 2,   Thus the area is Thus the area is   square unit and the perimeter is square unit and the perimeter is   . .
4. Draw
an equilateral triangle with height =   and label the vertices A, B, and C. Find the perimeter and area of the
triangle. and label the vertices A, B, and C. Find the perimeter and area of the
triangle.
ANS: By symmetry, AD = DB and height CD is perpendicular to AB
so AC = AB = 2AD and by the
Pythagoras’ theorem,     and AC
= 4. Thus the perimeter is 12 and
the area is and AC
= 4. Thus the perimeter is 12 and
the area is   square units. square units.
|
|
|
5. Given
the triangle shown at right, with AC
= AB and   ,
show that ,
show that  
ANS: The base angles of an isosceles
triangle are equal, so   . So by AAS, . So by AAS,   whence (CPCTC) EB =
DC and since whence (CPCTC) EB =
DC and since   the result the result   follows by SAS. follows by SAS.
|

|
|
6. The
figure at right is a parallelogram.
Find x.
ANS: These angles are supplementary,
so  
|

|
|
7. Find
the arc length that subtends a central angle of 60° in a circle of radius
12 cm.
ANS: Let the arc length be x.
Then since the arc length is in the same proportion to the
circumference as the central angle is to a complete rotation,  
|
|
8. Find
the area of region ACDB bounded
by concentric arcs
  = 4π cm and CD = 5π cm as shown at right. = 4π cm and CD = 5π cm as shown at right.
ANS: Since the arc length is in the
same proportion to the circumference as the central angle is to one
rotation,   cm and cm and   cm.
Thus the area of region ACDB is cm.
Thus the area of region ACDB is
  cm2 cm2
|

|
|
|
|
|
|