|
Math 5  Trigonometry Trigonometry  Chapter 1 Test Name__________________________ Chapter 1 Test Name__________________________
Show all work for credit.
Write all responses on separate paper.
|
1. Explain
why the two acute angles of a right triangle are complementary.
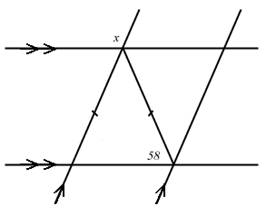
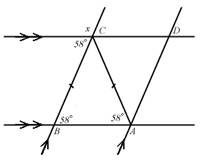
2. What
is the degree measure of angle x
in the figure at right? Explain how
you know.
3. True
or false: if one side of a quadrilateral is congruent to the opposite side,
then the quadrilateral is either a parallelogram or an isosceles
trapezoid. Justify your answer.
|
|
|
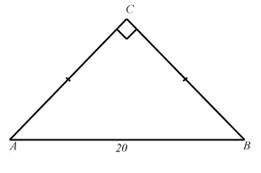
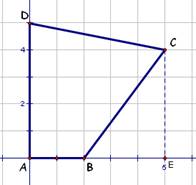
4. In
the isosceles right triangle shown at right,
AB = 20.
(a) What is the length of AC?
(b) Draw the altitude from
C to AB. What is its
length?
|
|
5.
Two boats leave a dock at the same time and at a 90o
angle from each other. After 3 hours one boat is 10 miles from the dock,
while the other is 40 miles from the dock. How far are the boats from each
other? Write your answer in simplest
radical form.
6.
Find the (a) perimeter and (b) area of a rectangle
with one side 10 cm and diagonal 13 cm.
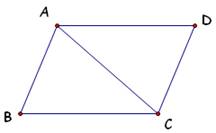
7.
Explain why a diagonal of a parallelogram creates two
congruent triangles.
|
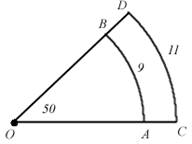
8. Find
the area of region ACDB.   = 9cm and CD = 11cm are concentric arcs with center O . = 9cm and CD = 11cm are concentric arcs with center O .
9. A
closed right circular cylinder has a radius of 3 meters. Find the volume of
the cylinder if its lateral surface area is 84π square meters. Leave your
answer in terms of π.
|
|
|
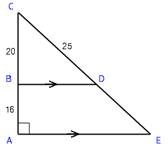
10. Show
that triangles BCD and ACE are similar and use that similarity to find the
length of DE in the diagram at right.
|
|
Math 5  Fall ’07 Fall ’07  Chapter 1 Test Solutions Chapter 1 Test Solutions
1.
Explain why the two acute angles of a right triangle
are complementary.
ANS: The sum of the interior angles of
any triangle is 180°. In a right
triangle, one angle is 90° and that means the remaining angles add up to 90°,
which means they’re complementary.
|
2. What
is the degree measure of angle x
in the figure at right? Explain how
you know
ANS: Since ΔABC is isosceles,   = 58°, and since = 58°, and since   ,
x must be supplementary to the
corresponding angle at C and thus
x = 122°. ,
x must be supplementary to the
corresponding angle at C and thus
x = 122°.
3. True
or false: if one side of a quadrilateral is congruent to the opposite side,
then the quadrilateral is either a parallelogram or an isosceles
trapezoid. Justify your answer.
ANS: False. Consider the
quadrilateral ABCD with vertices
at A(0,0), B(2,0), C(5,4) and D(0,5), as shown at right.
In the figure, AD = BC = 5, but the figure is neither a
parallelogram nor an isosceles trapezoid.
4. In
the isosceles right triangle shown at right, AB = 20.
(a) What is the length of AC?
ANS: AC/AB = AC/20 =   so so  
|
|
(b) Draw the altitude from C to AB. What is its length?
NS: This line would create two
congruent isosceles right triangles each half the size of the original. Thus the altitude would be 10.
5.
Two boats leave a dock at the same time and at a 90o
angle from each other. After 3 hours one boat is 10 miles from the dock,
while the other is 40 miles from the dock. How far are the boats from each
other? Write your answer in simplest
radical form.
ANS: The boats’ paths are legs of a
right triangle and the distance between them is the hypotenuse of that
triangle:  
6.
Find the (a) perimeter and (b) area of a rectangle
with one side 10 cm and diagonal 13 cm.
ANS: The short side of the rectangle is   so the perimeter is so the perimeter is   and the area is and the area is  
|
7. Explain
why a diagonal of a parallelogram creates two congruent triangles
ANS: The transversal AC forms
alternate interior angles congruent so that   . Also, AC
is congruent to itself. This establishes the conditions of the ASA so we
can conclude the triangles are congruent. . Also, AC
is congruent to itself. This establishes the conditions of the ASA so we
can conclude the triangles are congruent.
|
|
8.
Find the area of region ACDB.   = 9cm and CD = 11cm are concentric arcs with center O. = 9cm and CD = 11cm are concentric arcs with center O.
ANS: Solve the arc length formula   for the radius and plug in the values of s: for the radius and plug in the values of s:   and and   and then use these in the formula and then use these in the formula   for the area of a sector to compute the
difference of the sectors’ areas: for the area of a sector to compute the
difference of the sectors’ areas:   cm2. cm2.
9.
A closed right circular cylinder has a radius of 3
meters. Find the volume of the cylinder if its lateral surface area is 84π
square meters. Leave your answer in terms of π.
ANS: The formula for lateral surface
area is 2πrh. Substituting r = 3 and setting this equal to 84π we have 6πh = 84π whence h = 14, thus the volume is   . .
10. Show
that triangles BCD and ACE are similar and use that
similarity to find the length of DE
in the diagram.
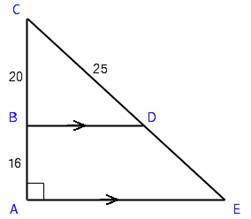
ANS: Since a transversal cutting parallel lines makes corresponding angles
congruent,   is a right angle. Also triangles BCD and ACE share an angle at A. Since two of the angles are equal, and the
sum of interior angles is 180°, it must be that the third angles are also
equal and thus the triangles are equiangular, which also means they are
similar. Let x = ED. Then, since corresponding parts of similar
triangles are proportional, is a right angle. Also triangles BCD and ACE share an angle at A. Since two of the angles are equal, and the
sum of interior angles is 180°, it must be that the third angles are also
equal and thus the triangles are equiangular, which also means they are
similar. Let x = ED. Then, since corresponding parts of similar
triangles are proportional,   . .
|







